REDs (Regenerative Energy Deposits)
REDs are the fundamental unit of measurement for uncompensated regenerative work.
Definition:
One (1.0) RED unit = 60 watt-hours of uncompensated human-controlled energy optimally spent aiding the earth's regenerative infrastructure (soil, water, air, and sunlight).
This value is based on the human basal metabolic rate - the energy we expend simply being alive.
Important: RETs document volunteer work, gig work, and personal regenerative efforts that receive no other compensation. If you're already being paid for the work through employment, grants, or government funding, it is not RET-eligible.
RETs (Regenerative Energy Receipts)
RETs are digital receipts documenting verified regenerative work.
Calculation:
RETs = REDs × P (Potency Index)
Potency Index (P): A multiplier (ranging from 0.5 to 4.0) that adjusts raw energy (REDs) to reflect ecological impact.
P-values serve two functions:
- Standardize value across different types of work
- Predict likelihood of successful ecological outcomes
Higher P-values reflect work with greater expected return-on-energy-investment in terms of biomass and biodiversity.
How It Works
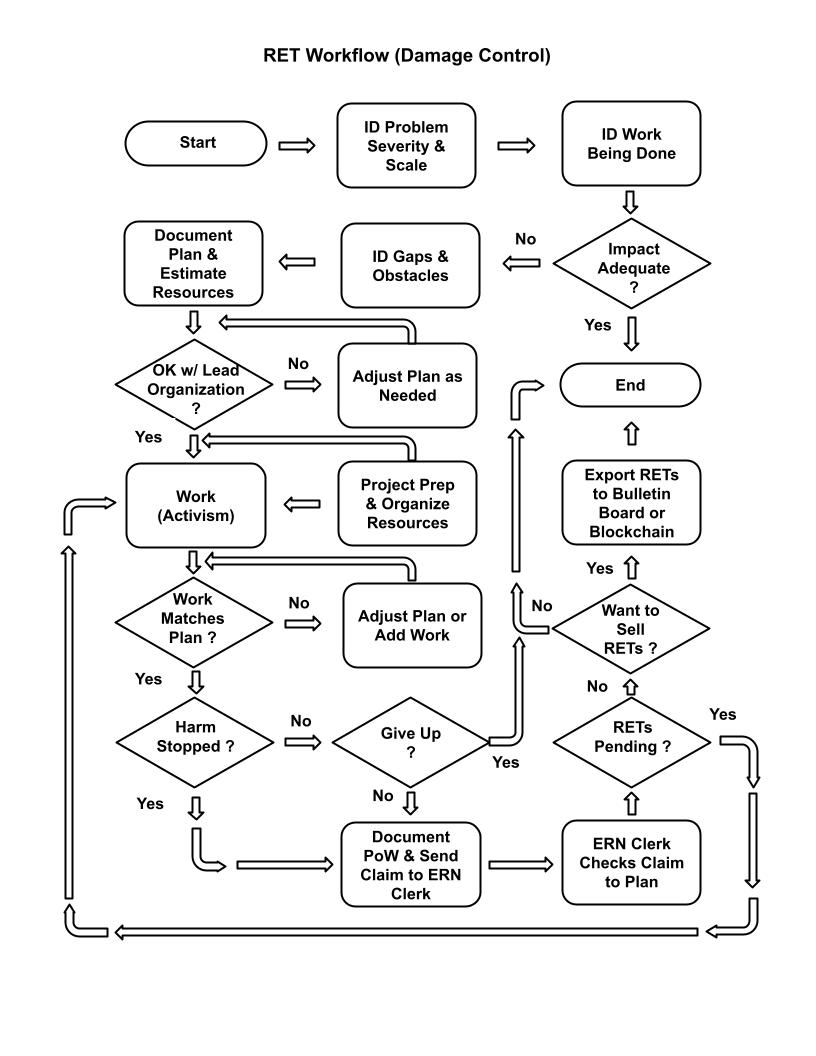
The ERN verification process documents uncompensated regenerative work and issues RETs as proof-of-work receipts.
Submit a Claim
Document your regenerative work with photos, location, and a completed claim form.
Verification
An ERN Inspector verifies the work on-site and confirms the evidence.
RETs Issued
The ERN Clerk calculates REDs, applies the P-value, and issues RETs to your account.
Transfer or Hold
RETs can be stored, transferred, or sold through independent peer-to-peer platforms.
Energy Workflow Diagram
Work Categories
Regenerative work is classified into five categories, each with specific criteria and P-value ranges:
Damage Control
Reducing or stopping environmental harm. Examples: removing invasive species, stopping erosion, cleaning up pollution.
Remediation
Undoing harm that has been done. Examples: soil restoration, water quality improvement, habitat recovery.
Maintenance
Protecting the local habitat. Examples: maintaining trails, managing vegetation, monitoring wildlife.
Upgrade
Enhancing habitat from the natural baseline. Examples: permaculture installations, native plantings, biodiversity enhancements.
System
Verification, documentation, and educational infrastructure work that enables the regenerative economy. Examples: inspector training, documentation systems, community education.